Information Technology
|
Forget DVDs, Welcome BRDs Mr. Kunj Vakil 06BCA63 (S.Y.B.C.A.)
|
|
Blu-ray
Disc In
1997, a new technology emerged that brought digital sound and video
into homes all over the world. It was called DVD, and it
revolutionized the movie industry. The
industry is set for yet another revolution with the introduction of
Blu-ray Discs (BD). With their high storage capacity, Blu-ray discs
can hold and play back large quantities of high-definition
video and audio, as well as photos, data and other digital
content. The
Blu-ray name is a combination of "blue", for the color of
the laser that is used, and "ray", for optical ray. The
"e" in "blue" was purposefully left off,
according to the manufacturers, because an everyday word cannot be trademarked What
is a Blu-ray Disc? A
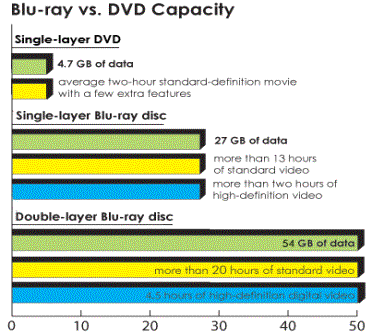
current, single-sided, standard DVD can hold 4.7 GB (gigabites) of
information. That's about the size of an average two-hour,
standard-definition movie with a few extra features. But a high-definition
movie, which has a much clearer image takes up about five
times more bandwidth and therefore requires a disc with about
five times more storage. As TV sets and movie studios make the move
to high definition, consumers are going to need playback systems
with a lot more storage
capacity
Blu-ray
has a higher data transfer rate -- 36 Mbps (megabits per second) --
than today's DVDs, which transfer at 10 Mbps. A Blu-ray disc can
record 25 GB of material in just over an hour and a half. Unlike
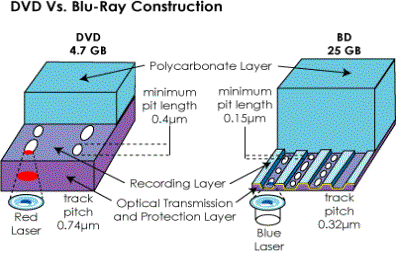
current DVDs, which use a red
laser to read and write data,
Blu-ray uses a blue laser (which is where the format gets its
name). A blue laser has a shorter
wavelength (405
nanometers) than a red laser (650 nanometers). The smaller
beam focuses more precisely, enabling it to read information
recorded in pits that are only 0.15 microns (Ám) (1 micron = 10-6 meters) long -- this
is more than twice as small as the pits on a DVD. Plus, Blu-ray has
reduced the track pitch
from 0.74 microns to 0.32
microns. The smaller pits, smaller beam and shorter track
pitch together enable a single-layer Blu-ray disc to hold more than
25 GB of information -- about five times the amount of information
that can be stored on a DVD.
Blu-ray
discs are better armed than current DVDs. They come equipped with a
secure encryption system -- a unique ID that protects against video
piracy and copyright infringement.
|
|