| .NET
Compact framework for mobile Computing Mr. Milind Contractor |
 |
|
.Net framework is now a day creating a big hike in the market. A person can able to make any kind of application using .Net framework. And one of such application is for the smart devices. The .NET Compact Framework is used to develop applications for smart devices. By smart devices we mean devices that run the Pocket PC 2000, Pocket PC 2002 and Windows CE.NET operating systems. These operating systems are targeted for mobile devices (like PDA, Pocket PC) that have small display areas, small storage areas and run on batteries. Developing
applications for devices has never been easier! Earlier,
people had to grapple with the eMbedded Visual Tools kit from
Microsoft. This toolkit essentially consists of an operating
system and development tools (like embedded Visual Basic and
embedded Visual C++). Application also had to deal with
different programming models and understand and work with the
API of the operating system. With the advent of the .NET
Compact Framework, Microsoft has unified the programming
models between developing applications for PC's and
applications for devices. The Introduction
to .NET Compact Framework The
.NET Compact Framework is a subset of the functionality found
in the .NET Framework. Major portions of the .NET Framework
were removed, since these did not make sense in the devices
world. When we say removed, it does not mean that the code was
simply cut-off and the remaining code got renamed as Compact
Framework :-) Microsoft re-wrote large chunks of the code to
take into account the form factor of small devices. Common
Language Runtime The
CLR is the most important part of the .NET Compact Framework.
It is responsible for taking a .NET assembly and then setting
up an application domain for it to run. A native just-in-time
(JIT) compiler is used to compile the MSIL code to the actual
machine bits. The CLR provides the services of memory
management, garbage collection and class loading. The CLR also
manages the security structure in which the application
executes. The
CLR consists of two parts. One is the direct execution
engine which is responsible for execution of the code and the
other is the base class libraries which is a set of reusable
classes that contain a basic set of building blocks that
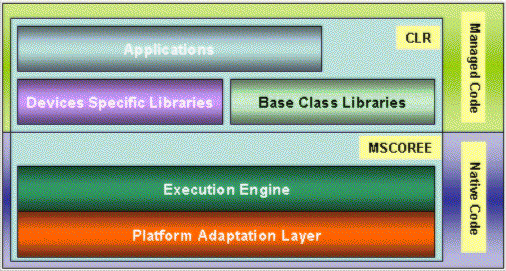
applications can use. The following figure shows a typical
construction of the .NET Compact Framework.
The
diagram is pretty straight forward.
These
two layers are packaged as a single executable called MSCOREE.
In
the .NET Compact Framework, there is one implementation of the
MSCOREE for each of the supported processors. If future
platforms become available with more capabilities, it is only
the PAL that needs to be changed, since it contains platform
specific features that will change between each hardware. Features
Missing From .NET Compact Framework As
mentioned earlier, the .NET Compact Framework is a subset of
the full .NET Framework and major sections were ignored
because they implemented features that were specific to the PC
platform, which did not make sense in the device world. The
following is a brief summary of the features that are excluded
from the .NET Compact Framework.
Availability
of .NET Compact Framework Visual
Studio .NET includes all the capabilities that allow you to
write and debug a device application (called Smart Device
Extensions). You use all the tools and techniques that are
available for developing normal application when writing
device applications too. Instead of using the .NET Framework
class libraries, you use the Compact Framework specific
libraries. Conclusion In
this article we have seen what exactly the .NET Compact
Framework is and where it is used. To develop a simple
application and how to deploy the application onto the device
one has to work on VS studio .NET. The Visual Studio .NET
development environment provides a very productive IDE for
developing smart-device applications and also provides
excellent emulation and debugging support. There are many
different types of applications that you can write using the
.NET Compact Framework and this hopefully helped you make a
good start to work with .NET compact framework. |
|